IC (Integrated Circuit) card was invented by French Roland Moreno in 1970. He put programmable IC chips in the card for the first time to make the card have more functions. "IC card" and "magnetic card" are both names from the technical point of view, and cannot be confused with "credit card", "telephone card" and other cards named from the application point of view. Since the emergence of IC card, there have been many international names for it. English names include "Smart Card", "IC Card", etc; In Asia, especially in Hong Kong and Taiwan, it is often referred to as "smart card", "smart card", "smart card", etc; In China, it is generally referred to as "IC card".
Ordinary IC card, sector 0 cannot be modified, and other sectors can be rewritten repeatedly. The smart card issuers such as elevator card and access card we use are all M1 cards, which can be understood as the original cards issued by the property.
UID card (GEN1 in foreign countries)
Common replication cards are mainly used for IC card replication. When a reader with a firewall is encountered, it will fail.
All blocks can be read and written repeatedly
The card ID can be changed and the ID can be changed using the backdoor instruction
ID can be modified repeatedly
Respond to the backdoor command (meaning that it can be detected by the machine that uses the backdoor command to detect whether it is a cloned card)
CUID card (GEN2 in foreign countries)
Erasable anti-shield card, which can repeatedly erase all sectors. It can be used when the UID card copy is invalid and can bypass the firewall. It does not need to lock the card to automatically play the role of anti-shielding. It can be repeatedly erased and used without waste card. It will not play the role of anti-shielding after FUID or UFUID is locked, and it will not become a one-time card because of card locking, and cannot change the data in the card to become a waste card.
All blocks can be read and written repeatedly
The card ID can be changed and the ID can be changed using ordinary writing instructions
ID can be modified repeatedly
Does not respond to backdoor commands (meaning it is not easy to be found by the anti-cloning system)
FUID card (GEN2 in foreign countries)
The non-erasable anti-shield card has the feature that sector 0 can only be written once, and it becomes an M1 card. It can be used when the CUID copy is useless and can bypass the firewall. However, once the FUID card is written to the backup dump file, it will solidify and lose the characteristics of the UID card
0 block can be written and can only be written once
Change ID with normal write instruction
More "anti cloning"
GTU/GUID/GDMIC card
The rolling code copying card is used for the elevator system of rolling code anti-copying, and the initial data written automatically after swiping the card.
Knowledge extension
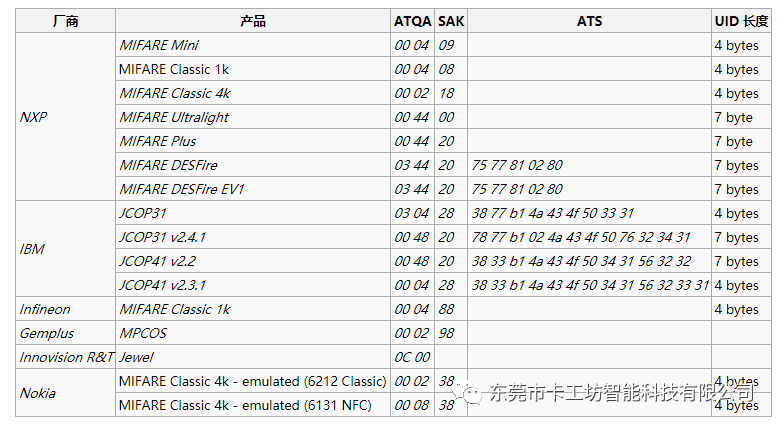
The sixth byte of sector 0 of the IC card data represents the chip type. The common IC card SAK type is: 08, the CPU analog card is: 28, and the pure CPU card is: 20
The following pictures collect some other unusual types of cards for your reference.